Impact
Apeiro Data Fabric
The Apeiro Data Fabric addresses the interoperability challenges across diverse software and service providers in the cloud, who offer complete business suites or modules, often with dedicated and incompatible technical stacks and platforms.
While providers may compete with their service and cloud offerings, joint customers still expect seamless, modular integration and demand interoperability between providers.
Customers and their businesses increasingly depend on making efficient, automated or AI-driven decisions based on dispersed datasets, hosted across different clouds and providers. Therefore, adopting a data driven mindset and understanding data as valuable resource requires a standard method for unform accessibility, regardless of where the data happens to reside.
We propose a set of standards and patterns that enable easy service consumption and discovery across multiple providers. To use data effectively and reliable it needs to be easily accessible through well-defined APIs and being grouped as meaningful business objects. Understanding how these business objects are related is crucial, as it bridges the gap between raw data and actionable insights, enabling more informed and strategic decisions. The projects contributed to the data fabric provide the needed accessibility and transparency in relationships between business objects in a multi-vendor scenario.
Data Fabric Concepts
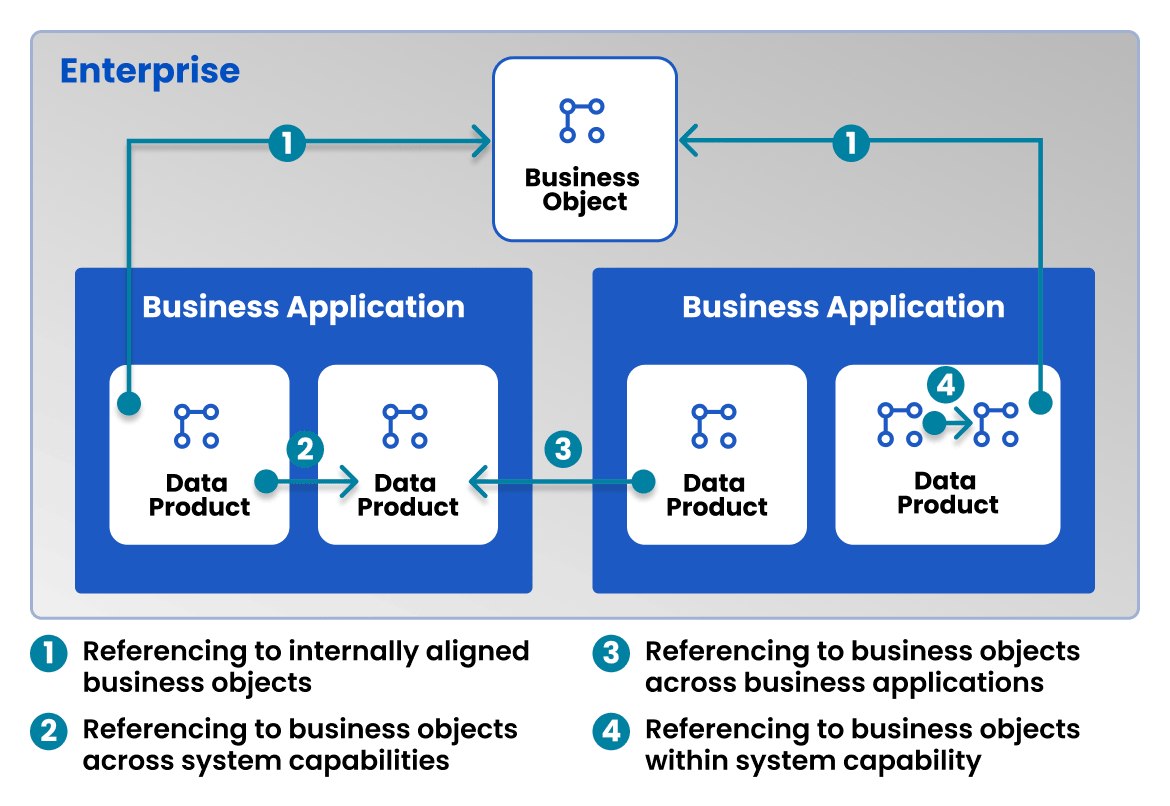
When thinking about how different systems and applications work together, customers often see business processes as moving through various independent departments, each with its own way of understanding key objects, like sales-orders or products. To put the information together we propose a decentralized self-description of application resources leading to a mesh architecture. It’s important to identify the correct business object (sales-order or product) behind any API, event, or data product. This helps define its meaning and find out which integration points are connected to the same business object. There are various ways business objects can be related, but we are introducing a standard generic option to create references across all possible scenarios.
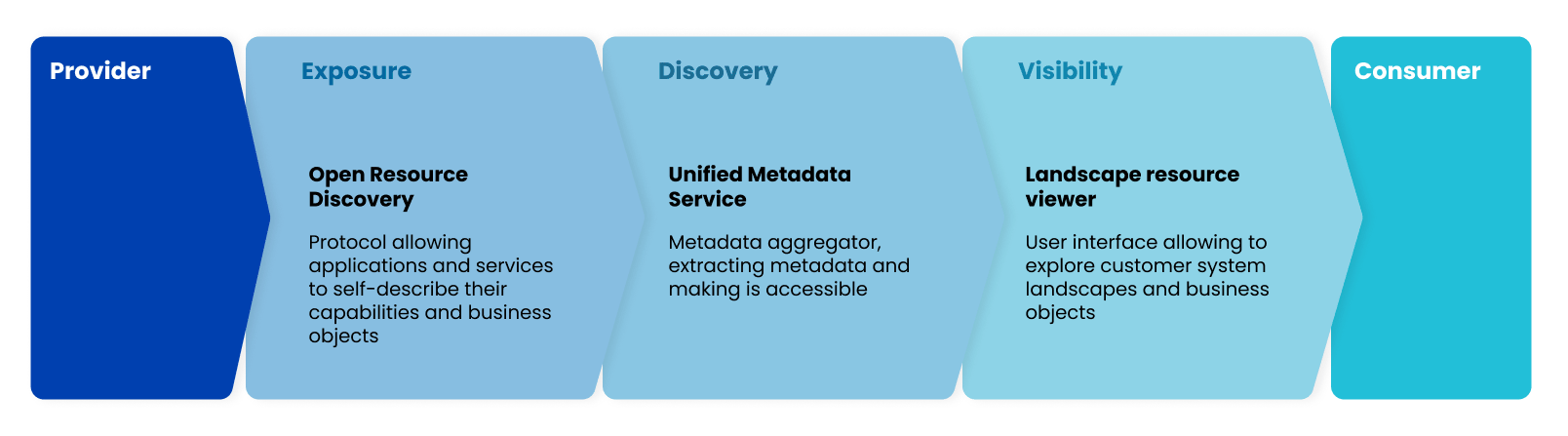
The following three projects are the main constituents of materializing the data fabric.
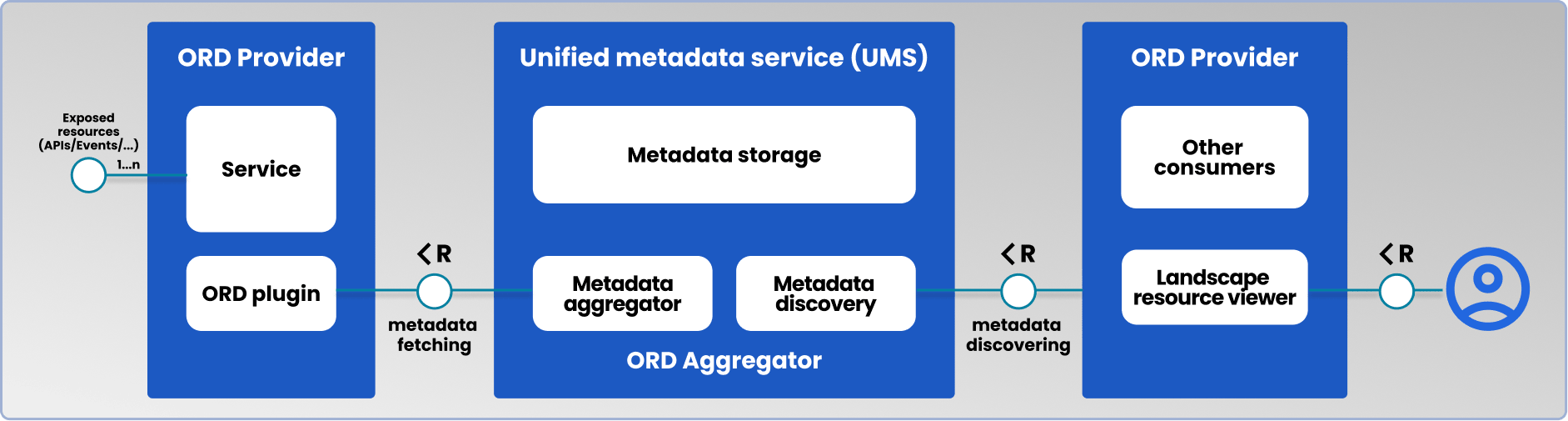
Open Resource Discovery (ORD)
ORD is a protocol providing a common standard to all vendors to describe their business applications by providing the metadata for a system capability (API, event, data product) and all available business objects including a description to provide context on those entity types. With an ORD endpoint, all metadata can be exposed in a standardized format. ORD also includes practical concepts and examples of how technical services can implement a business reality over a distributed cloud-edge scenario using ORD-based semantic concepts. ORD is fully contributed as open-source software, and a technical documentation is available here: Open Resource Discovery
Unified Metadata Service (UMS)
UMS is a central service that collects all ORD-based metadata of participating services. UMS itself, having collected and aggregated all metadata of a given customer landscape, in the broader context represents a Discovery API. This facilitates the automated understanding of how business objects are related across capabilities and business applications. Ultimately, ORD and UMS enable the seamless and automatic integration between services hosted across different providers.
Landscape Resource Viewer (LRV)
The landscape resource viewer helps visualize the aggregated metadata from UMS in a user-friendly user interface. LRV supports different target personas, like developers, IT expert and data analysts to comprehend a dynamically extensible service landscape, wherein all services expose and apply to the ORD standard. The displayed relationship model will be complemented by proper filter and search functionalities to quickly understand the definition of a business object and how it is connected to other entity types within the overall customer landscape. LRV is a functionality that helps drive adoption of the ORD standard.